
The Pomodoro Technique and ADHD: A Match Made in Heaven?
The Pomodoro Technique, a time management method involving 25-minute work intervals followed by short breaks, has gained popularity among individuals seeking to improve focus and productivity. But can this structured approach truly benefit those with ADHD, a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity?
This blog post will delve into the potential of the Pomodoro Technique for individuals with ADHD, exploring its potential benefits, limitations, and how to adapt it for optimal success.
Understanding the Challenges of ADHD and Productivity

Individuals with ADHD often face significant challenges when it comes to productivity.
- Distractibility: The constant bombardment of internal and external stimuli can easily derail focus, making it difficult to complete tasks.
- Procrastination: The fear of failure, perfectionism, and the overwhelming nature of tasks can lead to significant delays and avoidance.
- Time Blindness: Difficulty with time perception can make it challenging to estimate how long tasks will take, leading to poor planning and missed deadlines.
- Hyperfocus: While seemingly beneficial, hyperfocus can also be detrimental, as it can lead to excessive time spent on one task while neglecting others.
The Pomodoro Technique: A Potential Solution?

The core principle of the Pomodoro Technique is simple:
- Set a timer for 25 minutes.
- Work on a single task without interruption for the duration of the timer.
- Take a 5-minute break.
- Repeat steps 1-3 four times.
- Take a longer break (15-30 minutes).
This structured approach can offer several potential benefits for individuals with ADHD:
- Improved Focus: By breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks, the Pomodoro Technique can help to reduce feelings of overwhelm and improve focus.
- Increased Motivation: The short work intervals can provide a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue working.
- Reduced Procrastination: The structured nature of the technique can provide a framework for starting and completing tasks, making it less likely that individuals will procrastinate.
- Enhanced Time Management: By tracking time spent on tasks, individuals can gain a better understanding of their work habits and identify areas for improvement.
Adapting the Pomodoro Technique for ADHD
While the standard Pomodoro Technique can be beneficial, it may require some adjustments for individuals with ADHD:
- Adjusting Work Intervals:
- Some individuals with ADHD may find that 25-minute intervals are too long, while others may find them too short.
- Experiment with different interval lengths (e.g., 15 minutes, 20 minutes) to find what works best.
- Shortening Breaks:
- If frequent distractions are a significant issue, consider shortening the 5-minute breaks to 3 or 4 minutes.
- Visual Timers:
- Using a visual timer (e.g., a sand timer, a timer app with a visual countdown) can make the passage of time more concrete and help to maintain focus.
- Minimizing Distractions:
- Create a distraction-free environment by turning off notifications, silencing your phone, and finding a quiet workspace.
- Reward Yourself:
- Incorporate small rewards into your breaks to provide additional motivation and reinforce positive behavior.
Tools and Resources
Numerous tools and resources are available to help you implement the Pomodoro Technique:
- Timer Apps:
- Focus To-Do: A popular app that combines to-do lists with the Pomodoro Technique.
- Forest: An app that encourages focus by “planting” virtual trees that die if you leave the app.
- TomatoTimer: A simple and user-friendly timer app.
- Online Resources:
- Pomodoro Technique Website: The official website provides a wealth of information and resources.
- ADHD Blogs and Forums: Many online communities offer tips and strategies for adapting the Pomodoro Technique for ADHD.
The Importance of Self-Reflection
The Pomodoro Technique is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s crucial to experiment with different approaches and find what works best for you.
- Regularly review your progress:
- Track your work sessions, identify any patterns or challenges, and adjust your approach accordingly.
- Be patient and persistent:
- It may take time to find a rhythm that works for you. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately.
- Don’t be afraid to modify the technique:
- The Pomodoro Technique is a framework, not a rigid set of rules. Feel free to adapt it to fit your unique needs and preferences.
The Pomodoro Technique: A Valuable Tool, But Not a Cure-All
The Pomodoro Technique can be a valuable tool for individuals with ADHD, but it’s important to remember that it’s not a magic bullet.
- Address Underlying Issues:
- While the Pomodoro Technique can help to improve productivity, it’s essential to address any underlying issues that may be contributing to ADHD symptoms.
- This may include seeking professional help from a therapist, psychiatrist, or ADHD coach.
- Develop a Comprehensive Approach:
- The Pomodoro Technique is most effective when used in conjunction with other strategies for managing ADHD, such as medication, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
The Pomodoro Technique can be a valuable tool for individuals with ADHD, but it’s crucial to approach it with realistic expectations and a willingness to experiment. By adapting the technique to your unique needs and combining it with other strategies for managing ADHD, you can significantly improve your focus, productivity, and overall well-being.

Exploring the Role of Depression in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Two common mental disorders are often confused with each other and, therefore, hard to differentiate. These include post-traumatic stress disorder and depression. PTSD develops in a person after he or she has experienced some traumatic event. Depression can occur due to the emotional, psychological, and physiological impact of traumatic events. In this blog, we will explore the relationship between depression and PTSD, how one may exacerbate the other, and how both conditions can be treated effectively.
What is PTSD?

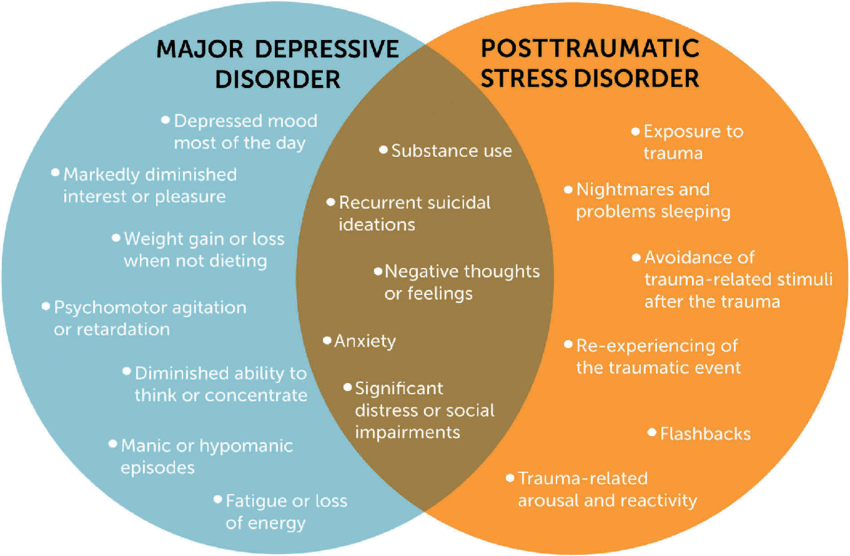
It is a kind of mental illness that follows exposure to traumatic events like combat experiences, natural disasters, or serious physical and sexual assault. The hallmark symptoms of PTSD are intrusive memories of the traumatic event, which people usually have nightmares about, flashbacks, emotional numbness, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, and heightened arousal symptoms such as irritability, difficulty sleeping, and hypervigilance.
What is Depression?
Depression, also known as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), is a mood disorder that causes persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in daily activities. Individuals with depression may experience fatigue, difficulty concentrating, changes in appetite, feelings of worthlessness, and suicidal thoughts. Unlike ordinary sadness, depression can significantly interfere with a person’s ability to function in daily life.
The Link Between PTSD and Depression
Although PTSD and depression are two different conditions, they share many similarities. Both disorders can be caused by trauma or significant stress, and many people with PTSD also have symptoms of depression. In fact, studies show that nearly 50-70% of people with PTSD also meet the criteria for a depression diagnosis.
Several factors contribute to the link between PTSD and depression:
The most common symptoms can include emotional numbness, irritability, sleep difficulty, and feeling hopeless in depression. The difficulty in distinguishing PTSD from depression also lies in shared symptoms.
Impairment in Emotional Regulation due to Trauma:
PTSD significantly impairs one’s ability to regulate emotions because an individual feels deserted, hopeless, or hopeless. These aspects are typical signs of depression which may develop out of the same trauma.
Negative Cognitive Patterns:
Trauma is associated with negative thinking patterns that may lead to depression. For instance, individuals suffering from PTSD are always stuck with the feelings of guilt, shame, or worthlessness. These negative feelings can prevent the healing process and contribute to depression.
Physical and Biological Factors:
Both PTSD and depression may be related to the chemical and structural changes of the brain. Chronic stress caused by trauma can alter the balance of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine in controlling moods. The changes in brain function may predispose an individual to develop both PTSD and depression.
Avoidance and Social Isolation:
One of the fundamental symptoms of PTSD is an urge to avoid reminders of the traumatic event, which may lead to social withdrawal and isolation. This avoidance behavior may, therefore, contribute to the feelings of loneliness and sadness central to depression.
Loss of Meaning and Purpose:
After experiencing trauma, many individuals struggle with feelings of purposelessness. The inability to find meaning in life following a traumatic event can contribute to the onset of depression, especially if the individual is unable to process the trauma or move forward.
The Impact of Depression on PTSD
When depression is comorbid with PTSD, it can significantly worsen the course of the disorder. Depression may hinder the ability to cope with the trauma, making recovery more challenging. The combination of PTSD and depression can lead to:
- An increase in suicide is also associated with both PTSD and depression. Where these two problems occur together, suicide ideation or behavior is extremely high. Someone suffering from these two problems often feels trapped into their emotional suffering and cannot escape.
- Worsened Functionality: Depression can worsen the symptoms of PTSD by lowering motivation, energy levels, and interest in activities. This may lead to loss of social connections, decreased productivity, and impaired daily functioning.
- The symptoms of depression can further intensify emotional numbness and detachment in PTSD. When the symptoms are added together, the individual may experience a sense of separation from themselves and others, making it hard to deal with emotions and memories connected to the trauma.
- Impaired Recovery: Depression might slow down recovery in PTSD. The feeling of hopelessness and despair that develops with depression could make it impossible for individuals to engage in appropriate treatment or coping strategies for PTSD.
Treatment of PTSD and Depression
When PTSD and depression occur together, it’s essential to treat both conditions simultaneously. Addressing one without considering the other may lead to incomplete recovery. Here are some effective treatments for managing PTSD and depression:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT is one of the most used therapies for PTSD and depression. The therapy helps an individual identify negative thought patterns and challenge them. It replaces negative thoughts with healthy ones and builds coping strategies. For PTSD, the same approach can be taken to address thoughts and memories that may be related to trauma.
Trauma-Focused Therapy:
Specialized therapies, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), can help people process traumatic memories. These therapies are especially effective for PTSD and can reduce the intensity of trauma-related symptoms, leading to less emotional distress.
Medication:
Patients are put on antidepressants, usually SSRIs or SNRIs, to cure both PTSD and depression. Medications help level out the brain chemical and control mood. Sometimes, sleeping problems or anxiety are assisted by the use of medications for a patient who happens to have these conditions.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques:
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, can help individuals with PTSD and depression manage stress and anxiety. These techniques can improve emotional regulation, enhance self-awareness, and promote relaxation, which is beneficial for both conditions.
Social Support:
A strong support network is very important for individuals with PTSD and depression. Talking to trusted family members, friends, or support groups can provide emotional relief, reduce isolation, and encourage recovery.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle habits including regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep can support good mental health along with recovery from depression and PTSD. Its changes can affect mood, increase energy, and help reduce both conditions’ symptoms.
Conclusion
The relationship between PTSD and depression is complex and multifaceted. They can be precipitated by trauma, share overlapping symptoms, and feed off each other, so both need to be treated together. Through therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes, people can control both PTSD and depression, thereby improving their emotional well-being and quality of life.
If you, or someone around you, has PTSD and depression, then recovery is the very first step you need to undertake. Healing with the right kind of support and care is indeed possible, and one will be able to regain control over life.

5 Things You Should Avoid Doing When You Have Anxiety
Anxiety can feel overwhelming, affecting your thoughts, emotions, and even your physical well-being. While managing anxiety involves learning healthy coping strategies, it’s equally important to recognize and avoid behaviors that can worsen your symptoms. Here are five things you should avoid doing when you’re experiencing anxiety, along with practical advice to navigate these challenges effectively.
What is Anxiety?

Anxiety is a widespread mental health condition that can significantly impact daily life, causing persistent worry, restlessness, and physical symptoms like rapid heart rate or difficulty concentrating. While managing anxiety often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, therapy, and relaxation techniques, medication can be a vital part of treatment for those experiencing more severe symptoms. Ativan (Lorazepam) is a commonly prescribed medication that works quickly to alleviate feelings of anxiety by calming the nervous system. Its fast-acting nature provides relief, helping individuals regain control over their emotions and manage stress more effectively. For those seeking a reliable solution, purchasing Ativan online with secure delivery options can offer a convenient way to access the medication and take the first step toward better mental well-being.
5 Things You Should Avoid Doing When You Have Anxiety
Anxiety can feel overwhelming, affecting your thoughts, emotions, and even your physical well-being. While managing anxiety involves learning healthy coping strategies, it’s equally important to recognize and avoid behaviors that can worsen your symptoms. Here are five things you should avoid doing when you’re experiencing anxiety, along with practical advice to navigate these challenges effectively.
1. Avoiding the Source of Your Anxiety
When something makes you anxious, the natural response is often to avoid it. Whether it’s a social situation, a work task, or even a tough conversation, avoidance provides temporary relief but often worsens anxiety over time. By dodging what triggers your discomfort, you miss the opportunity to build confidence and resilience.
Why It’s Harmful:
- Avoidance reinforces the idea that the situation is dangerous or unmanageable.
- It limits your personal growth and prevents you from developing coping skills.
- Over time, avoidance can shrink your comfort zone, making it harder to face everyday challenges.
What to Do Instead:
- Practice Gradual Exposure: Break the situation into smaller, manageable steps. For example, if public speaking makes you anxious, start by speaking to a small group of trusted friends before tackling a larger audience.
- Seek Support: Share your concerns with a therapist or trusted individual who can guide you through confronting your fears.
- Reward Progress: Celebrate small victories as you face your anxiety triggers, reinforcing positive associations.
2. Overindulging in Stimulants like Caffeine or Nicotine

When dealing with anxiety, reaching for that extra cup of coffee or indulging in a cigarette may seem like a way to stay alert or calm down. However, stimulants like caffeine and nicotine can amplify the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as a racing heart, jitteriness, and restlessness.
Why It’s Harmful:
- Caffeine increases adrenaline levels, mimicking the body’s stress response and making anxiety feel more intense.
- Nicotine, while initially calming, creates a cycle of dependence that can worsen overall stress levels.
- Overuse of stimulants can disrupt sleep, which is critical for managing anxiety.
What to Do Instead:
- Limit Stimulant Intake: Switch to decaffeinated coffee, herbal tea, or other caffeine-free beverages. Gradually reduce your intake to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
- Find Healthier Alternatives: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to naturally calm your mind and body.
- Prioritize Sleep: Create a nighttime routine that promotes restful sleep, such as avoiding screens an hour before bed and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
3. Engaging in Negative Self-Talk
Your inner dialogue plays a significant role in how you perceive and manage anxiety. If you often criticize yourself, assume the worst, or engage in “what-if” thinking, you’re likely feeding your anxiety rather than calming it.
Why It’s Harmful:
- Negative self-talk fuels self-doubt and feelings of helplessness.
- It distorts your perception of reality, making problems appear larger than they are.
- Constant criticism can erode your self-esteem, increasing vulnerability to anxiety.
What to Do Instead:
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: When you catch yourself thinking negatively, ask yourself if there’s evidence to support these thoughts. Replace them with more balanced and realistic perspectives.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Treat yourself as you would a friend. Offer kindness, encouragement, and patience rather than harsh criticism.
- Use Affirmations: Incorporate positive affirmations into your daily routine, such as “I am capable of managing challenges” or “I am doing my best.”
4. Isolating Yourself
When anxiety takes hold, you may feel tempted to retreat from the world and spend time alone. While short periods of solitude can be restorative, prolonged isolation often exacerbates anxiety by allowing negative thoughts to spiral unchecked.
Why It’s Harmful:
- Isolation reduces access to social support, which is crucial for emotional well-being.
- Spending too much time alone can lead to rumination, a cycle of overthinking that worsens anxiety.
- Loneliness can intensify feelings of disconnection and helplessness.
What to Do Instead:
- Stay Connected: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups. Even a simple conversation can lift your mood and provide perspective.
- Engage in Activities: Join clubs, classes, or community events that align with your interests to foster a sense of belonging.
- Schedule Social Time: Plan regular meetups or phone calls with loved ones to ensure you maintain consistent social interaction.
5. Trying to Handle Everything Alone
Anxiety often comes with a sense of personal responsibility to “fix” everything on your own. While self-reliance is admirable, refusing to seek help can leave you feeling stuck and overwhelmed.
Why It’s Harmful:
- Tackling anxiety without support can lead to burnout and feelings of hopelessness.
- You may miss out on valuable insights, strategies, or treatments that could alleviate your symptoms.
- Struggling alone reinforces the misconception that asking for help is a sign of weakness.
What to Do Instead:
- Reach Out for Professional Help: Therapists, counselors, and support groups offer specialized guidance and tools to help you manage anxiety effectively.
- Confide in Trusted Individuals: Share your experiences with someone you trust, whether it’s a friend, partner, or family member. They may provide emotional support or practical solutions you hadn’t considered.
- Explore Resources: Books, online courses, and apps focused on anxiety management can supplement professional help and empower you to take control of your mental health.
Conclusion
Managing anxiety isn’t just about adopting positive behaviors—it’s also about avoiding habits that can worsen your symptoms. By confronting your fears, limiting stimulants, fostering positive self-talk, staying connected, and seeking support, you can create a healthier and more balanced approach to anxiety. Remember, progress takes time and effort, but with consistent practice and the right tools, you can regain control and find peace amidst the challenges. Take that first step today—your future self will thank you.

8 Benefits of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
Sleep plays an essential role in our physical and mental well-being, yet millions of people struggle with insomnia. Insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, can affect productivity, mood, and overall health. While there are various treatments available, one proven and highly effective method is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I). Unlike medications that address symptoms, CBT-I focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of insomnia. Let’s explore the eight major benefits of this transformative therapy.
Breaking Down Insomnia: Causes and Solutions

Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, can leave you tossing and turning at night while draining your energy and focus during the day. It often stems from stress, anxiety, poor sleep habits, or underlying health conditions. If left untreated, it can take a toll on your mental and physical well-being.
The good news? Insomnia is manageable. Small changes, like creating a calming bedtime routine, limiting caffeine, and sticking to a consistent sleep schedule, can significantly improve your sleep quality. For persistent cases, therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) provide a science-backed, drug-free solution to reclaim restful nights.
Sleep is vital for a healthy, balanced life. Prioritize it today and unlock the benefits of better rest and
8 Benefits of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia

1. Addresses the Root Cause of Insomnia
CBT-I goes beyond treating the symptoms of sleeplessness and identifies the psychological and behavioral factors contributing to insomnia. Negative thought patterns, such as “I will never fall asleep,” and poor sleep habits, like inconsistent bedtime routines, are common triggers. CBT-I helps you recognize these patterns and replace them with positive and constructive habits that promote long-term sleep health. By targeting the underlying causes, it ensures more sustainable results than temporary fixes offered by medication.
2. Non-Invasive and Drug-Free
One of the standout benefits of CBT-I is that it is entirely drug-free. While medications for insomnia can offer temporary relief, they often come with risks such as dependency, side effects, or reduced effectiveness over time. CBT-I eliminates these concerns by providing a natural and non-invasive way to improve sleep. This approach makes it suitable for individuals who prefer to avoid pharmaceuticals or those who have experienced negative side effects from sleep medications.
3. Improves Sleep Quality
CBT-I doesn’t just help you fall asleep faster; it also enhances the quality of your sleep. Through techniques like stimulus control and sleep restriction therapy, it encourages deeper, more restorative sleep cycles. Stimulus control teaches you to associate your bed with sleep and relaxation rather than wakefulness or stress. Sleep restriction therapy limits the amount of time you spend in bed initially, gradually increasing it as your sleep efficiency improves. Over time, these strategies lead to a more rejuvenating sleep experience.
4. Promotes Long-Term Benefits
Unlike quick fixes, CBT-I equips you with tools and strategies that promote lasting results. The skills you learn during therapy sessions—like managing stress, developing healthy bedtime routines, and challenging negative thoughts—can be used throughout your life. Studies show that the benefits of CBT-I often persist long after the therapy has ended, making it a valuable investment in your overall well-being.
5. Reduces Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are common culprits behind sleepless nights. CBT-I addresses these issues by teaching relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness help calm your mind and body, reducing the physical tension that prevents sleep. By challenging and reframing anxious thoughts about sleep, CBT-I helps create a more peaceful mental state, making it easier to drift off.
6. Customizable and Individualized Approach
CBT-I is tailored to meet your specific needs and challenges. A trained therapist works with you to identify your unique sleep patterns, triggers, and goals. This personalized approach ensures that the strategies are relevant and effective for your situation. Whether you struggle with falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early, CBT-I adapts to address your particular concerns.
7. Improves Daytime Functioning
Insomnia doesn’t just affect your nights; it takes a toll on your days as well. Fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and reduced productivity are common daytime consequences of poor sleep. By improving the quality and consistency of your sleep, CBT-I helps restore your energy and focus during the day. You’ll find it easier to perform daily tasks, engage in social interactions, and maintain a positive mood.
8. Evidence-Based and Backed by Research
CBT-I is one of the most extensively studied treatments for insomnia, with a strong track record of success. Research consistently shows that it is as effective—if not more effective—than medication for improving sleep. Moreover, its benefits extend beyond sleep, with many participants reporting improved mental health and reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression. Organizations like the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the National Institutes of Health endorse CBT-I as a first-line treatment for insomnia.
How CBT-I Works: Key Components
To fully understand the benefits of CBT-I, it’s helpful to know how it works. The therapy typically includes the following components:
- Sleep Education: Learning about the sleep cycle, how much sleep you need, and how behaviors and thoughts influence your sleep.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs about sleep.
- Stimulus Control: Creating a strong association between your bed and sleep by avoiding activities like watching TV or using your phone in bed.
- Sleep Restriction: Regulating your time in bed to improve sleep efficiency.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing strategies to calm your mind and body, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Sleep Hygiene: Developing healthy bedtime routines and optimizing your sleep environment.
Who Can Benefit from CBT-I?
CBT-I is effective for a wide range of people, including those who:
- Struggle with chronic or acute insomnia
- Experience insomnia alongside anxiety or depression
- Have difficulty discontinuing sleep medications
- Want to avoid dependency on sleep aids
- Are looking for long-term solutions to improve sleep quality
Tips for Starting CBT-I
If you’re considering CBT-I, here are some steps to get started:
- Consult a Sleep Specialist: Reach out to a therapist or healthcare provider trained in CBT-I.
- Track Your Sleep: Keep a sleep diary to identify patterns and triggers.
- Be Patient: CBT-I requires commitment and consistency, but the results are worth the effort.
- Practice Regularly: Apply the techniques you learn during therapy to reinforce new habits.
Conclusion
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia offers a comprehensive and effective solution for improving sleep. Addressing the root causes of insomnia and equipping you with lasting skills, it enhances not only your sleep but also your overall quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with chronic insomnia or occasional sleepless nights, CBT-I provides a safe, natural, and evidence-based path to better sleep. Take the first step toward restful nights and rejuvenated days by exploring this transformative therapy.

Dealing with Insomnia During the Winter Months: Seasonal Sleep Struggles
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can occur during any time of the year, many individuals find that their sleep struggles intensify during the winter months. The shorter days, longer nights, colder temperatures, and changes in daily routines brought about by the winter season can significantly impact our sleep patterns, leaving us tossing and turning at night. Understanding the causes of winter-related insomnia and implementing effective strategies can help you achieve better rest and improve your overall well-being.
Why Is Insomnia More Common in Winter?

Several factors contribute to the rise in sleep issues during winter:
- Reduced Exposure to Natural Light: During winter, daylight hours are shorter, and many people spend most of their time indoors due to the cold weather. This reduced exposure to natural sunlight can disrupt the body’s circadian rhythm, the internal clock that regulates sleep and wake cycles. Without adequate sunlight, the production of melatonin (a hormone responsible for sleep) may increase during the day, leading to daytime lethargy and nighttime restlessness.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): Seasonal Affective Disordersirt, often referred to as the “winter blues,” is a type of depression that typically occurs during the colder months. Symptoms of SAD include fatigue, low energy, and difficulty sleeping. The lack of sunlight is believed to play a significant role in triggering this condition, which can exacerbate insomnia.
- Colder Temperatures: While cooler temperatures are generally ideal for sleep, extreme cold can have the opposite effect. If your bedroom is too cold or your bedding isn’t adequate, you may find it difficult to stay comfortable and fall asleep.
- Holiday Stress and Disruptions: The winter season brings holidays and celebrations, which can lead to irregular schedules, increased stress, and overindulgence in food and drinks. These factors can disrupt your sleep routine and make it harder to get quality rest.
- Changes in Physical Activity: Many people become less active during the winter due to the cold weather and shorter days. Reduced physical activity can lead to pent-up energy, making it harder to unwind at night.
Tips for Managing Insomnia During Winter
Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to combat winter insomnia and improve your sleep quality:
1. Maximize Exposure to Natural Light
Since daylight hours are limited during winter, it’s crucial to make the most of the available sunlight. Spend time outdoors during the day, especially in the morning. Even a short walk outside can help regulate your circadian rhythm and boost your mood. If getting outside isn’t an option, consider using a light therapy box, which mimics natural sunlight and can help combat the effects of Seasonal Affective Disorder.
2. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Establishing a regular sleep routine is one of the most effective ways to combat insomnia. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends and holidays. Consistency helps reinforce your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and makes it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
3. Create a Cozy Sleep Environment
Your bedroom should be a sanctuary for sleep, especially during the winter months. Keep your room at a comfortable temperature, ideally between 60-67°F (15-19°C). Use warm, breathable bedding and consider layering blankets so you can adjust your comfort level throughout the night. Block out any external light with blackout curtains and minimize noise with earplugs or a white noise machine.
4. Stay Physically Active
Regular exercise is a powerful tool for improving sleep quality, reducing stress, and boosting overall health. During winter, find indoor activities like yoga, pilates, or home workout routines to stay active. Just make sure to avoid vigorous exercise too close to bedtime, as it may leave you feeling energized and delay sleep onset.
5. Limit Screen Time Before Bed
The blue light emitted by phones, tablets, and computers can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt your circadian rhythm. To prepare your mind and body for sleep, avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime. Instead, opt for relaxing activities like reading a book, listening to soothing music, or practicing meditation.
6. Watch Your Diet and Hydration
What you eat and drink can have a significant impact on your sleep quality. Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime. While alcohol might make you feel drowsy initially, it can disrupt your sleep cycle and lead to poor-quality rest. Instead, opt for a light, healthy snack if you’re hungry, and stay hydrated throughout the day without overdoing it right before bed.
7. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Winter can be a stressful season, and managing stress is crucial for overcoming insomnia. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery into your nighttime routine. These practices can help calm your mind, release tension, and prepare your body for restful sleep.
8. Use Aromatherapy to Promote Relaxation
Certain scents, like lavender, chamomile, and sandalwood, are known for their calming properties. Consider using essential oils, candles, or a diffuser in your bedroom to create a soothing atmosphere that promotes relaxation and sleep.
9. Consider Professional Help
If your insomnia persists despite trying these strategies, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. A doctor or sleep specialist can help identify underlying causes and recommend treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), medications, or other interventions tailored to your needs.
The Importance of Self-Care During Winter

Dealing with insomnia during the winter months can be challenging, but prioritizing self-care can make a significant difference. Ensure you’re taking time to nurture your mental and physical health by engaging in activities that bring you joy, connecting with loved ones, and seeking support when needed. Remember that winter is a temporary season, and with the right strategies in place, you can overcome sleep struggles and feel more rested and refreshed.
Final Thoughts
Winter’s shorter days and colder nights can make sleep more elusive for many people. However, understanding the factors contributing to insomnia during this season and taking proactive steps to address them can help you achieve better rest. By maximizing your exposure to natural light, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a cozy sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques, you can enjoy a more restful winter. If insomnia persists, don’t hesitate to seek professional help to ensure you’re getting the quality sleep your body and mind need to thrive.
